90% of the world’s data was created in the last two years.
This explosion of gigabytes, terabytes, and our insatiable appetite for them has created some big cybersecurity problems, but the opportunities for those who can solve them are even more massive.
The Problem
Its not just that the amount of data the world produces is doubling in size every two years, which poses its own set of infrastructure-related problems.
Its that organizations are legally obligated to protect user data from being lost, stolen, or compromised in any way.
Such compliance costs carry a huge price tag.
Although hard to quantify, the chief strategy officer of one data analytics company believes the cost of fully complying with various data protection laws such as the EU’s comprehensive General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) is north of $30 million.
But if you think compliance is expensive, try non-compliance.
Its cost could be nearly double, in terms of lost business and fines.
A few notable examples of major data breaches include…
Yahoo’s 3 Billion Accounts
First, who knew Yahoo counted over a quarter of the world’s population as users!
Second, the odds of hackers being able to breach the same database not just once, but on multiple occasions over the course of three years, must have been miniscule, yet it happened, which means it could happen again.
Russian hackers allegedly pulled off the operation using backdoors, stolen back up codes, and access cookies to reach Yahoo’s database, stealing user names, passwords, and security questions.
Faced with unknown costs from the breaches, Yahoo and Verizon mutually agreed to a $350 million reduction in the price Verizon would pay for Yahoo’s business.
Stealing more than Home Depot’s Hardware
If one of the world’s largest internet companies with top of the line IT systems in place was vulnerable to a major cyber attack, than a predominantly brick and mortar retailer such as Home Depot was like taking a pacifier from a baby.
In a showcase of just how sophisticated an attack can be, it was determined that perpetrators ultimately accessed Home Depot servers through a third-party supplier site and then were able to install malware on the retail chain’s Point-of-Sale systems.
This redirected the payment info of approximately 56 million customers to a third-party server that belonged to the hackers.
All told, the April 2014 attack cost Home Depot an estimated $180 million in customer payouts and lawsuit settlements.
Australian Ports Brought to A Standstill
In a more recent example, the operations of four major ports in Australia had to be shut down this past November following a crippling cyberattack.
The container terminals of DP World Australia located in Sydney, Melbourne, Brisbane, and Fremantle handle around 5,000 containers on any given day and account for 40% of all goods entering the country.
Following the breach, the operator had to disconnect its servers from the internet for three days to prevent any additional unauthorized access to its systems.
Such a standstill cost it “millions of dollars per day.”
But these are just a few prominent examples of what the FBI’s Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3) approximates are $12.5 billion in annual losses due to cyber crime.
As large as this figure is, it pales in comparison to the size of the cybersecurity opportunity.
The Opportunity
Disturbingly, the number of global cyberattacks is not only increasing, but they are also becoming more and more intricate in nature.
From 2021 to 2022, the number of attacks increased by 38% and a further 20% from 2022 to 2023, leading some to say that cyberattacks are outstripping our ability to deal with them.
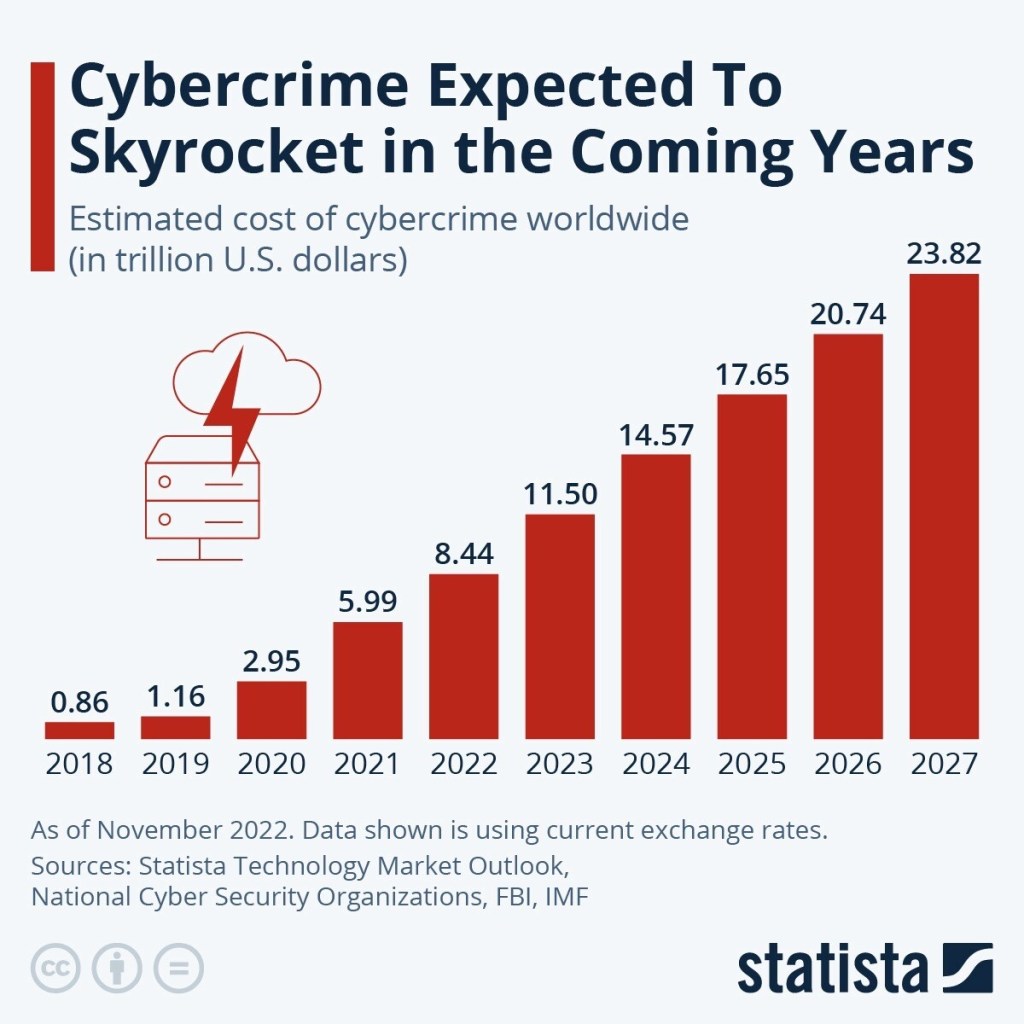
Its a big reason why cybersecurity has become a $2 trillion market.
This may all sound like the prefix to a dystopian cyberpunk future, but all is not lost.
The answer lies in the very thing cyberattacks seek to exploit – data, and what is better at analyzing and learning from vast amounts of data than Artificial Intelligence?
From having the capacity to identify statistical anomalies before they become attacks in real-time to automating responses to incidents, AI is a threat to the shadowy multi-billion-dollar business of cyberattacks.
The First Use Case
Early, crude versions of artificial intelligence first began to be applied to cybersecurity systems in the early 2000s.
These were little more than algorithms built to analyze network traffic patterns and detect anomalies, but it was an important step that would be built upon.
Now, with computing capabilities being vastly greater, the full power of AI can finally be applied to dealing with online threats and a few early-stage firms are stepping up and doing this in a big way.
The Solution
One of the best early examples of AI being applied to cybersecurity is its original use case – threat detection and prevention.
As some firms have unfortunately found out, traditional threat detection methods can take hours or more than a day to identify a problem.
In today’s world, a cyberattack happens every 39 seconds, meaning cybersecurity systems need to be able to identify and respond to threats in real time.
No Hacking Small Businesses
Huntress’ managed cybersecurity platform provides full endpoint visibility, threat detection, and response to the segment most vulnerable and susceptible to cyberattacks – small and medium-sized businesses.
Now SMB’s can have a 24/7 fully managed and monitored cybersecurity solution just like a large enterprise, all for an affordable price.
With a 99% customer satisfaction rate and less than 1% false positive detection rate, Huntress is a tried and true solution.
Fighting AI with AI
Threats are constantly evolving, so its a must for defense systems to keep up and evolve along with them.
Cadenza-back Jericho Security is doing this with a unique model.
Imagine this, it’s the middle of the day and you’re sitting at your desk when you receive an innocent-looking email from one of your vendors.
It offers you a discount on products you are already purchasing from them and a link to buy them at a reduced rate. Thinking you’re getting a deal, you excitedly click the link and your screen goes completely blank.
You have just been hit with an automated phishing attack.
Jericho helps to prevent such a scenario from ever happening by empowering organizations to defend themselves against the latest cyberattack techniques with its AI-powered cyber security training for employees.
Aimed at mid to large-size businesses with dedicated IT staff already in place, Jericho’s training platform provides hyper-realistic, personalized attack simulations with its phishing simulation platform.
Given that generative AI’s ability to mimic human communication and create ‘deep fakes’ is growing by the day, Jericho Security is a first line of defense against such emerging threats.
By the time you read this, a new cyberthreat has likely emerged that didn’t exist yesterday, which is why AI may not just be the best way to deal with such accelerated risks, but indeed it may be the only way.
If you found this informative, you may also like Thoughts on Generative AI or The Cloud & AI Combo: Groundbreaking or Trouble?
If you would like more information on our thesis surrounding Cybersecurity, AI, or other transformative technologies, please email info@cadenza.vc


2 responses to “Guardians of the Digital Galaxy: How AI is Changing Cybersecurity”
[…] portfolio company, Jericho Security, which we have previously written about and who created cyberGPT for enterprise cybersecurity. It is a prime example of domain-specific […]
LikeLike
[…] you found this insightful, you will also like Guardians of the Digital Galaxy: How AI is Changing Cybersecurity and Digital Gold Rush: How Digital Assets Are Ushering In A New Era of Financial Freedom in Latin […]
LikeLike